Biodiversity month day 18: Biodiversity and Sustainable Agriculture
The relationship between biodiversity and sustainable agriculture is integral to ensuring the long-term health and productivity of agricultural systems.
The St. Maarten Hospitality & Trade Association supports the March Biodiversity awareness month organized by the Nature Foundation in an effort to help protect St. Maartens nature and biodiversity. Todays topic: Biodiversity and Sustainable Agriculture
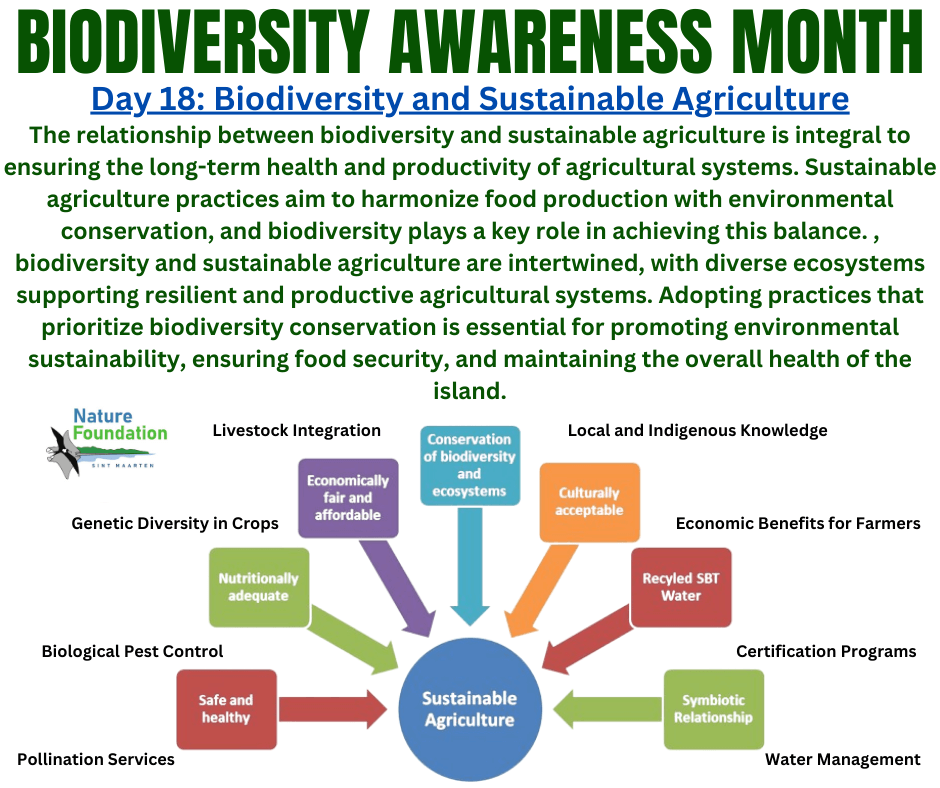
Sustainable agriculture practices aim to harmonize food production with environmental conservation, and biodiversity plays a key role in achieving this balance. Here are several ways in which biodiversity and sustainable agriculture are interconnected:
1. Pollination Services: Biodiversity, particularly in the form of pollinators such as bees, butterflies, and other insects, is crucial for pollination in many crops. Pollinators contribute to increased yields and quality of fruits, vegetables, and nuts. Maintaining diverse habitats around agricultural fields supports pollinator populations.
2. Biological Pest Control: Biodiversity can provide natural pest control through the presence of beneficial insects, birds, and other organisms that prey on or parasitize crop pests. This reduces the reliance on chemical pesticides, promoting healthier ecosystems and reducing the risk of harm to non-target species.
3. Genetic Diversity in Crops: Biodiversity within crop species, known as genetic diversity, is essential for the resilience of agriculture. Diverse crop varieties can adapt to changing environmental conditions, pests, and diseases. Preserving traditional and heirloom varieties helps maintain genetic diversity.
4. Agroforestry and Biodiversity Corridors: Agroforestry practices, which integrate trees and shrubs into agricultural landscapes, contribute to biodiversity by providing habitats for birds, insects, and other wildlife. Biodiversity corridors connecting natural habitats can enhance ecosystem connectivity and support biodiversity within agricultural landscapes.
5. Cover Crops and Crop Rotation: The use of cover crops and crop rotation promotes biodiversity in the soil. Cover crops prevent soil erosion, fix nitrogen, and improve soil structure. Crop rotation helps break pest and disease cycles, reducing the need for chemical inputs.
6. Conservation Agriculture: Practices such as minimal tillage, cover cropping, and diverse crop rotations are components of conservation agriculture. These practices contribute to soil health, water conservation, and the preservation of beneficial soil organisms, fostering biodiversity in agricultural landscapes.
7. Livestock Integration: Integrating livestock into agricultural systems can contribute to biodiversity. Well-managed rotational grazing systems, for example, mimic natural ecosystems, promoting healthy grasslands and benefiting both livestock and wildlife.
8. Local and Indigenous Knowledge: Indigenous and local agricultural practices often incorporate traditional knowledge that respects and enhances biodiversity. This knowledge can involve planting diverse crops, using agroecological methods, and adapting cultivation practices to local ecosystems.
9. Water Management: Sustainable agriculture practices aim to conserve water resources, which in turn supports aquatic biodiversity. Implementing efficient irrigation systems, reducing water runoff, and protecting water quality contribute to the health of aquatic ecosystems.
10. Certification Programs: Biodiversity considerations are increasingly integrated into agricultural certification programs. Certifications such as organic farming and Rainforest Alliance incorporate biodiversity criteria to ensure that agricultural practices are environmentally sustainable.
11. Economic Benefits for Farmers: Sustainable agriculture practices that enhance biodiversity can provide economic benefits for farmers. Increased crop yields, reduced input costs, and improved resilience to environmental changes contribute to the long-term viability of agricultural operations.
In summary, biodiversity and sustainable agriculture are intertwined, with diverse ecosystems supporting resilient and productive agricultural systems. Adopting practices that prioritize biodiversity conservation is essential for promoting environmental sustainability, ensuring food security, and maintaining the overall health of the planet.
Back to the Visit St Maarten Main page