Biodiversity month day 23: Biodiversity, Insects and Pollinators
The St. Maarten Hospitality & Trade Association supports the March Biodiversity awareness month organized by the Nature Foundation in an effort to help protect St. Maartens nature and biodiversity. Todays topic: Biodiversity, Insects and Pollinators
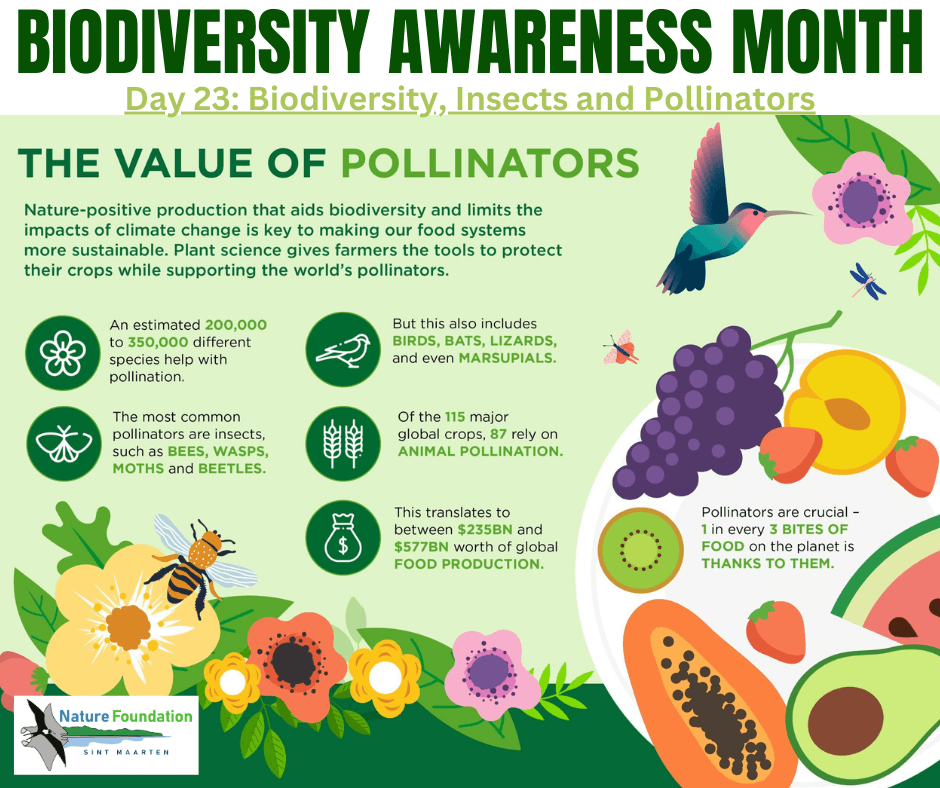
Biodiversity, especially in the context of insects and pollinators, is crucial for maintaining healthy ecosystems and supporting global food production. Insects, including various pollinators, play essential roles in the reproduction of flowering plants, contribute to ecosystem services, and are integral to the overall diversity of life on Earth. Here are key points highlighting the relationships among biodiversity, insects, and pollinators:
1. Pollination Services: Many plants, including numerous crops, depend on insects for pollination. Pollinators, such as bees, butterflies, moths, and beetles, transfer pollen between flowers, enabling the fertilization and production of seeds and fruits. This process is critical for the reproduction of flowering plants and the production of diverse food crops.
2. Plant Diversity: Insects contribute to the maintenance of plant diversity by facilitating cross-pollination among different plant species. This process leads to the genetic variability of plant populations, supporting their adaptation and resilience to changing environmental conditions.
3. Food Web Dynamics: Insects form an integral part of food webs, serving as prey for various animals, including birds, amphibians, reptiles, and mammals. Their presence and diversity contribute to the stability and balance of ecosystems.
4. Ecosystem Services: Insects provide essential ecosystem services beyond pollination, such as decomposition, nutrient cycling, and pest control. Decomposer insects, like beetles and ants, break down organic matter, contributing to soil health and nutrient cycling.
5. Cultural and Aesthetic Value: Insects, including butterflies and dragonflies, have cultural and aesthetic value. They are often admired for their diverse colors, patterns, and behaviors, and their presence contributes to the beauty of natural environments.
6. Bioindicators: Insects serve as bioindicators of environmental health. Changes in insect populations can reflect shifts in ecosystem dynamics, pollution levels, and climate change impacts, providing valuable insights into the overall well-being of ecosystems.
7. Biodiversity Hotspots: Insect diversity is particularly high in biodiversity hotspots, which are regions with a concentration of endemic species. Protecting these hotspots is crucial for conserving the diversity of insect species and, by extension, the broader biodiversity of these areas.
8. Genetic Diversity: Insect populations contribute to genetic diversity within their species. This genetic variability is essential for adaptation to changing environmental conditions, including the ability to resist diseases and cope with climate fluctuations.
9. Crop Pollination and Agricultural Productivity: Insects, especially bees, play a key role in pollinating many crops, including fruits, vegetables, and nuts. This direct contribution to agricultural productivity underscores the economic importance of insect pollinators for food security.
10. Threats to Pollinators: The decline in pollinator populations, including bees and butterflies, poses a significant threat to biodiversity and global food production. Factors such as habitat loss, pesticide use, climate change, and diseases contribute to the decline in pollinator populations.
11. Conservation Efforts: Conservation efforts focused on insects and pollinators include the protection of natural habitats, creation of pollinator-friendly landscapes, reduction of pesticide use, and initiatives to raise awareness about the importance of insect biodiversity.
12. Scientific Research and Monitoring: Ongoing scientific research and monitoring programs are essential for understanding insect biodiversity, assessing population trends, and identifying factors influencing insect health. This knowledge informs conservation strategies and policies.
In summary, the intricate relationships among biodiversity, insects, and pollinators highlight the interconnectedness of life on Earth. Protecting and promoting insect biodiversity is crucial for maintaining ecosystem health, supporting food production, and preserving the overall richness of global biodiversity.
Back to the Visit St Maarten Main page